Fixed Wing drones are entirely different in design. They use a ‘wing’ just like the normal airplanes out there. Instead, they move forward on their set course or as set by the guide control (possibly a foreign unit operated by a human) as long as their energy source permits.
Most fixed-wing drones have a mean flying time of a few hours. Internal combustion engine-powered drones can fly up to 16 hours or higher. But they will not be used for aerial photography where the drone must be kept still on the air for a period of your time.
What types of force operate fix wing drone:
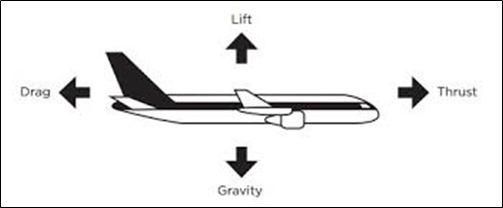
Four main forces are operating on an aircraft while on the wing. These are:
- Lift
- Gravity
- Drag
- Thrust
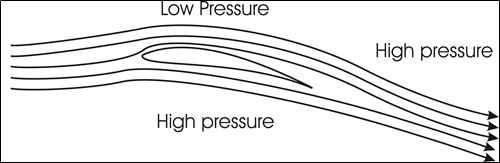
Not only are these forces present on fixed-wing aircraft, but also all the opposite categories are presented. To know how the lift is generated a cross-sectional view of the wing and therefore the airflow surrounding the wing is analyzed. This cross-sectional view of the wing is named an “airfoil”.
As shown above, the airfoil creates a neighborhood of low on the highest surface of the airfoil and a neighborhood of high on the lower surface. This is often caused by the airfoil shape “turning” the flow downward. As a result, the airflow over the top of the site generates a low-pressure region causing the wing to be lifted upward.
The control of an aircraft are;
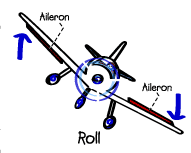
Roll- This maneuver will rotate the wings right or left around the fuselage of the aircraft.
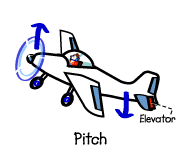
Pitch – this is often what makes the aircraft climb and descend.
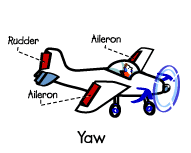
Yaw- this is often the turning of the airplane. This maneuver points the nose of the aircraft to the proper or left.
Each of those maneuvers is a result of moving the control surfaces on the aircraft. The three main control surfaces on an aircraft are:
Ailerons – control the roll of the aircraft.
Rudder- Control the yaw of the aircraft.
Elevators – control the pitch of the aircraft.
Can a Fixed-Wing be utilized in Negative Ways?
The fixed-wing category of UAVs is that the most diverse as far as payload types, range, endurance, and what they will be used for. For instance the usefulness of the fixed-wing category, this text will break down the fixed-wing aircraft supported size to spotlight what each size category is usually utilized for.
- Large fixed-wing (10lbs or higher)
- Medium fixed-wing (2lbs-10lbs)
- Small fixed-wing (2lbs or less)
Fixed Wing Flight Benefits
- Long-range and endurance
- High altitude is capable of creating detection difficult
- Can carry relatively heavy objects
- Quiet during operation
Looking at this UAV from a security standpoint, this model might be used for various missions:
- Surveillance - Mounting a camera on the rock bottom of the fixed-wing provides a stable platform for top altitude photography.
- Flying Weaponry – This model can easily be retrofitted to hold a gun and programmed to fireside at the command of the pilot.
- Dropping Supplies/Explosives – These fixed-wing aircraft are often retrofitted to hold supplies and explosives which will be dropped from a high-altitude design to impact a selected target. This makes for difficult detection and with long-range and high endurance capabilities little chance of the pilot being discovered.
Large Fixed-Wing
Large fixed-wing UAVs generally have a high endurance, long-range, and high payload capacity. There are many various sorts of these platforms available on the market today. For a general idea of the performance of this class of UAVs, the My TwinDream 1.8m UAV was selected.
The battery utilized in this specific aircraft may be a 14.8v Lithium Polymer (Li-Po) 20Ah battery. This aircraft features a “cruising current” of 10 Amps. Below this, the flight time is 1.5 hrs.
Medium Fixed-Wing
Medium Fixed-W- Wing UAVs generally have high endurance, long-range, and low payload capacity. This is often presumably the foremost popular fixed-wing size range available on the market today. For a general overview of the performance which will be seen from this UAV class, the Volant Firstar V2 is highlighted.
This aircraft features a wingspan of roughly 80” and weighs around 7 pounds with no payload. The utmost sized battery which will be used with this aircraft may be a 14.8v 20Ah Lithium Polymer battery. This can mean the Firstar has an endurance of 1.5 hours. Since this aircraft’s propeller pitch and motor Ki are slightly above the long-range aircraft this platform features a longer range of roughly 100 miles.
Small fixed-wing
Small fixed-wing UAVs generally is capable of long endurance and long-range flights. However, they lack the specified wing area necessary to hold large amounts of payload. For the tiny fixed-wing category, the Strip Nano Goblin is highlighted.

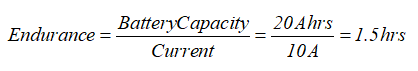


Comments
Post a Comment